Co-processing Biomass and Plastics with SH Scientific’s Rotary Kiln
Practical Approaches to Waste-to-Energy and Sustainable Hydrogen Production
Globally, industries are increasingly seeking innovative solutions to convert waste materials into valuable resources such as fuels, clean energy, and recyclable materials.
Two illustrative examples highlighting the promise of these approaches are Mexico’s Petgas and the UK’s Mura Technology:
- Petgas (Mexico) currently processes approximately 1.5 tons of plastic waste weekly, producing roughly 1,350 liters of liquid fuels (such as gasoline and diesel). After an initial propane startup phase, the process becomes self-sustaining by using gases produced internally.
- Mura Technology (UK) employs an advanced hydrothermal recycling process to convert mixed plastic waste into valuable hydrocarbon feedstocks like oils and chemicals. These feedstocks are then supplied to downstream partners such as Dow and Neste, who further process them into new, virgin-grade plastics suitable for food-contact applications. While Mura itself does not directly produce food-grade plastics, its process is a critical step enabling a circular economy for plastics.
These examples illustrate scalable pathways for waste management, resource recovery, and environmental sustainability.
Why Combine Biomass and Plastics?
Biomass and plastics differ significantly in their composition and properties, yet combining them in thermal processes offers distinct advantages:
- Biomass: Derived from organic sources, contains high oxygen levels and exhibits excellent reactivity, allowing it to decompose quickly.
- Plastics: Petroleum-based synthetic polymers, including polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyethylene (PE), and polypropylene (PP), characterized by high calorific (energy) value.
When biomass and plastics undergo co-processing via pyrolysis or gasification, the interaction provides several benefits:
- Improved reaction speed: Biomass accelerates the decomposition reaction.
- Enhanced energy efficiency: Plastics supply significant thermal energy, facilitating better decomposition of biomass.
SH Scientific’s rotary kiln facilitates these co-processing experiments by precisely controlling heat transfer, reaction rates, and environmental conditions.
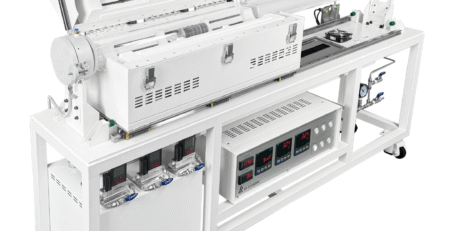
Spotlight on SH Scientific’s Rotary Kiln Technology
SH Scientific’s laboratory-scale rotary kiln is engineered to support versatile thermal processing experiments, including pyrolysis and gasification processes involving biomass and plastics. Specifically, SH Scientific’s kiln provides researchers with the following capabilities:
- Versatile Atmosphere Control: The kiln accommodates multiple atmospheres, including nitrogen, steam, carbon dioxide, or air, allowing precise control for diverse thermal decomposition processes.
- Uniform Temperature Control: Ensures ±3 °C temperature uniformity, critical for reliable, repeatable experimental results.
- Real-Time Analytical Capabilities: Built-in ports facilitate immediate gas analysis using techniques such as gas chromatography (GC), mass spectrometry (MS), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR).
- Scalable Internal Design: Interchangeable internal geometries closely mimic commercial-scale rotary kilns, supporting realistic scale-up from laboratory to industrial applications.
By offering a flexible and precise experimental platform, SH Scientific’s rotary kiln enables thorough research into co-processing technologies.
Steam Gasification for Hydrogen Production
Steam gasification involves reacting solid fuels (e.g., biomass) with high-temperature steam to produce synthesis gas (syngas) consisting predominantly of hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and methane (CH₄).
The advantages of steam gasification include:
- Clean Hydrogen Production: Syngas produced can be directly utilized for clean hydrogen production.
- Potential for Carbon Capture: By coupling steam gasification with CO₂ capture technologies, it is possible to generate low-carbon or even carbon-negative hydrogen.
SH Scientific’s rotary kiln can effectively support steam gasification studies by allowing precise control of reaction conditions, enabling researchers to analyze syngas composition, hydrogen purity, and carbon capture potential.
Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF): Practical Waste-to-Energy Implementation
Blending biomass and plastics creates Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF), a critical component of waste-to-energy systems. RDF efficiently transforms diverse waste materials into useful energy sources, significantly reducing landfill usage and environmental harm.
SH Scientific’s rotary kiln provides an optimal experimental setup to examine RDF properties and optimize reaction conditions, maximizing energy output while minimizing by-products.
Real-World Implications and Environmental Benefits
Practical implementations by companies such as Petgas and Mura Technology demonstrate the real-world effectiveness and environmental advantages of co-processing biomass and plastics. Petgas directly produces fuels from plastic waste, whereas Mura’s innovative recycling process contributes valuable feedstocks that partners transform into virgin-grade plastics, facilitating a circular plastics economy.
The laboratory-scale research enabled by SH Scientific’s rotary kiln technology is vital for understanding and optimizing these waste-to-energy processes. By allowing accurate simulation of commercial operations, researchers and industry stakeholders can generate precise data for techno-economic analysis, life-cycle assessments, and informed scalability decisions.
Ultimately, these co-processing strategies not only contribute significantly to environmental sustainability and resource efficiency but also provide a practical foundation for further innovation and commercial viability in the global pursuit of sustainable energy solutions.