Tube Furnace
A tube furnace is an essential piece of equipment in the fields of material science, chemistry, and engineering, serving a pivotal role in controlled, high-temperature processing. Characterized by their cylindrical heating chambers, tube furnaces are designed to uniformly heat materials placed within them. The inception of these furnaces traces back to the early 20th century, driven by the demand for precise temperature control in a variety of industrial and scientific research applications.
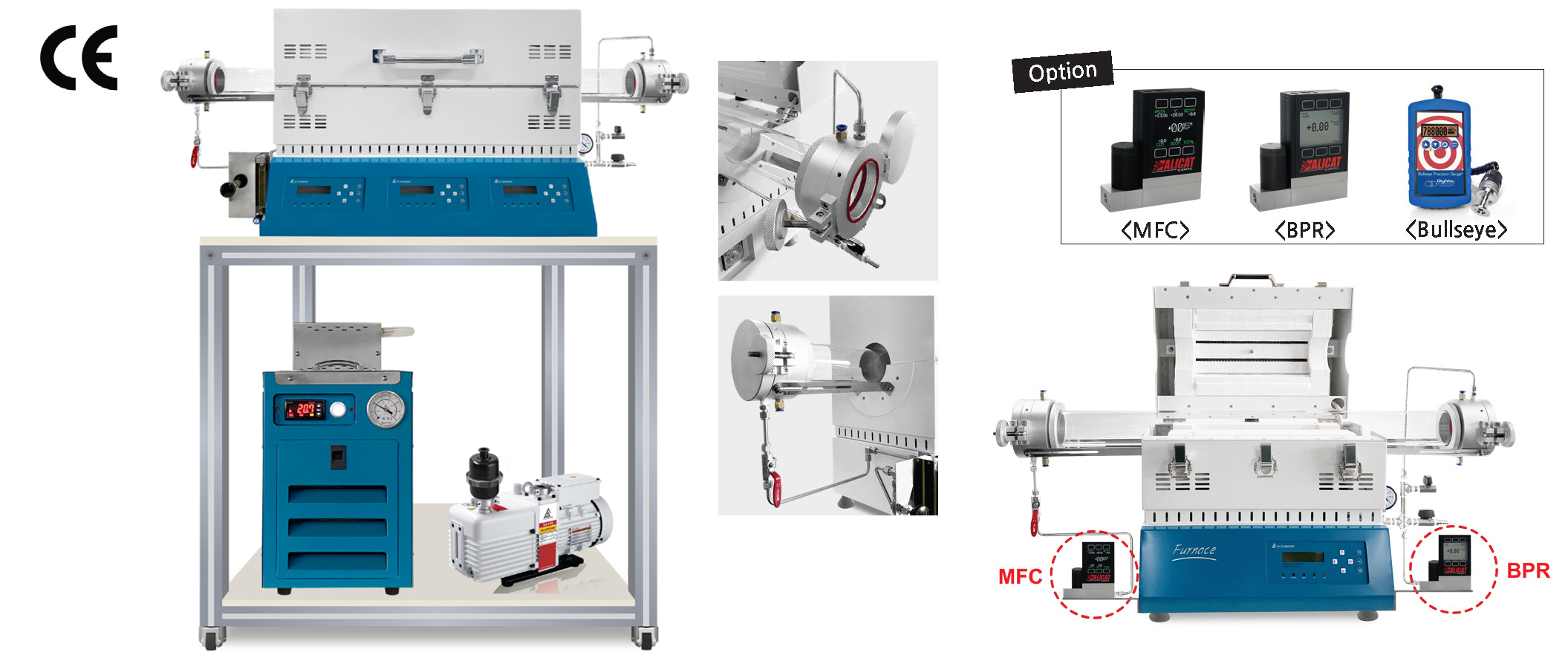
Types and Applications
Standard Tube Furnace

Critical for uniform heating, these are widely utilized in research laboratories and industrial settings for material processing.
Quartz Tube Furnace

Commonly utilized in laboratories, instructional labs, and research centers. Quartz tubes offer additional advantages in research environments that generate corrosive gases, as they are more resistant to chemical corrosion.
Alumina Tube Furnace

Known for their high-temperature capabilities and excellent thermal conductivity, suitable for calcination and sintering processes.
Vacuum Tube Furnace

Crucial for conducting materials research in reduced atmospheres or specific gas environments.
High Vacuum Tube Furnace
The high vacuum tube furnace can maintain pressures below 10^-7 torr, essential for minimizing oxidation and other gas-related reactions to prevent contamination. This capability is crucial in fields like materials science and nanotechnology, where precise atmospheric control is necessary for accurate material studies and synthesis.
High Temperature Tube Furnace

High temperature tube furnaces are specifically designed to achieve extremely high temperatures, often up to 1800°C or more. This capability allows processing materials that require very high heat, such as advanced ceramics and material synthesis.
Laboratory-scale Rotary Kiln

Laboratory rotary kilns are often used for pilot-scale studies or small production runs in research and development labs in industries. It typically operate under ambient atmospheric conditions or sometimes under a controlled but not completely vacuumed environment.
Vacuum Rotary Tube Furnace
Similar in basic design to rotary kilns, these furnaces have additional features to maintain a vacuum and control the atmosphere inside. Vacuum rotary furnaces provide superior temperature and environmental control, which is crucial for processing materials that are highly reactive or require high purity.
Historical Development and Technological Advancements
The development of tube furnaces reflects significant advancements in material science and industrial processing techniques. From their initial applications in basic heat treatment to their current sophisticated uses in semiconductor manufacturing, advanced ceramics, and metallurgical processes, tube furnaces have evolved into highly versatile and capable instruments.
SH Scientific’s Global Presence and Contributions
Established in 1982 in South Korea, SH Scientific has become a leader in tube furnace technology. The strategic establishment of its U.S. headquarters in 2018 responded to global demands for its innovative and versatile products, aiming to enhance access to SH Scientific’s cutting-edge technology, particularly for sectors focused on environmental sustainability and energy efficiency.
SH Scientific has established partnerships with prominent entities such as Samsung, Hyundai, Cornell University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), University of Texas, Illinois Institute of Technology, SpaceX, and Northrop Grumman. These collaborations underline SH Scientific’s dedication to fostering advanced research and development across diverse sectors, including automotive, aerospace, higher education, and federal research initiatives.
